Choosing which tree to plant on their plot, many summer residents experience difficulties associated with limited space - it is almost impossible to comfortably place a house, a garden, a vegetable garden and a resting place on 5-6 hundred square meters. Dwarf varieties of fruit trees can come to the rescue, which, having a small and compact crown, give excellent yields at the same time. A vivid example of this is the apple tree of the Lingonberry variety, which will be discussed later.
Description of apple lingonberry
Lingonberry - the variety is quite old. It appeared in the second half of the last century as a result of the work of breeders of the Russian Agricultural Academy, or rather, the All-Russian Selection and Technology Institute of Gardening and Nursery, located in Moscow.
Did you know? In ancient Greek mythology, there is a “version” that the true reason for the Trojan War was not at all the abduction of the beautiful Elena Paris, but a quarrel that broke out between the three goddesses - Athena, Hero and Aphrodite. And the apple was the reason for the argument.
Interestingly, the genetic formula of Lingonberry is not fully known: the fruit tree, which successfully passed state tests in 1977, is a seedling accidentally grown as a result of free pollination of the Ukrainian apple tree of the Slava Pobediteley variety, characterized by strong growth and high yield, unidentified Malus domestica variety (apple tree home). Nevertheless, the hybrid that turned out to be very successful has a specific author - A.V. Petrov.

In the State Register of Breeding Achievements of Russia, the Brusnichnoye variety was included in 2001 and zoned in the 3rd tolerance region. This means that the apple tree is recommended for cultivation in the Central region - in the Moscow, Bryansk, Ivanovo, Kaluga, Vladimir, Tula, Smolensk and Ryazan regions of the Russian Federation.
Good results are also shown by the Brusnichny landing in most regions of the Volga-Vyatka region of Russia, as well as in regions with a warmer climate, including in the Caucasus and Ukraine.
Important! Lingonberry apple tree is often grafted onto a dwarf rootstock, which makes it possible to grow an even more compact tree than a root seedling of this variety. At the same time, the yield of such trees even exceeds the usual indicators for Lingonberry.
The main feature of the variety is the shape of the tree. It is always stunted (dwarf), does not grow above 2-3 m. The crown is spreading, not very thickened, weeping, which gives the tree a very decorative look. The branches are rather thin, weakly overgrown (annual growth usually does not exceed 7 cm). Fruiting is mixed: the fruits are tied both on simple gloves and on spears and spurs.
Flowering time is the end of May, and fruiting is the turn of summer and autumn. The plant enters the fruiting phase very early: the first apples on the tree may appear as early as the next year after planting, if they are not removed on time. Productivity is high, without pronounced cyclicality.

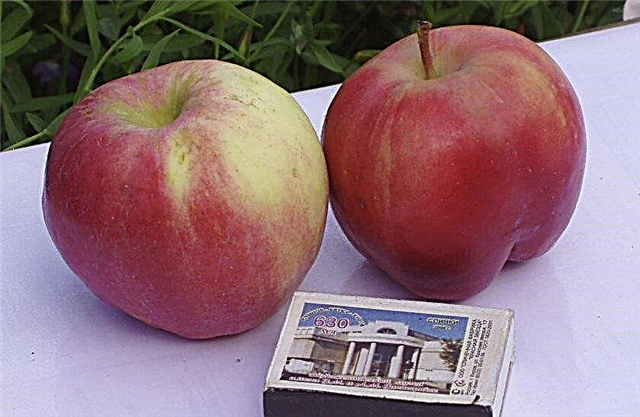
Describing the fruits of Lingonberry, it is necessary to highlight their main characteristics:
| Dimensions | Small, no more than 80–120 g |
| The form | Cylindrical elongated |
| Peel | Thin, with a glossy wax coating, light yellow with a blurry bright raspberry blush over almost the entire area |
| Peduncle | Thin, short |
| Pulp | Creamy, coarse-grained, medium density. |
| Taste | Delicate, juicy, sweet and sour, with a delicate, barely noticeable aroma |
| Appointment | Universal (can be consumed fresh, squeezed juices, used to make jam, other types of preservation, as well as ferment, freeze or dry) |
| Tasting rating | 4.5–5 points on a five-point scale |
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- The main advantages of the variety are:
- stunted and compact tree;
- the rapid onset of fruiting (especially in seedlings grafted onto clonal stocks) and its regularity;
- very high yields (up to 150 kg per tree that has reached 8 years of age);
- high winter hardiness;
- resistance to scab and most other fungal infections;
- beautiful appearance of the fruit;
- excellent taste characteristics.
 Immaturity, fruiting stability and high productivity allow us to attribute the Lingonberry apple tree to varieties of the intensive type.
Immaturity, fruiting stability and high productivity allow us to attribute the Lingonberry apple tree to varieties of the intensive type.
- Among the disadvantages of the variety are:
- small fruition;
- the tendency of the fruit to fall;
- moderate resistance to cytosporosis and fruit rot;
- high requirements for soil composition, light, moisture (does not tolerate both drought and stagnation of water in the soil);
- dependence on pollinators (low ability to pollinate with their own pollen);
- short shelf life of the crop;
- the short life of the tree itself.
Landing Features
When choosing a place for a dwarf apple tree on a site, you should be guided by the following rules:
| Lighting | Maximum: the tree should be in direct sunlight for at least 6 hours a day |
| Ground water | Minimum 1.5 m, maximum 3.5 m from the ground |
| Side on the site | Better south (to protect against north wind) |
| The soil | Fertile, porous, light, with good water and air permeability. Recommended pH is 5.1–7.5 (neutral or slightly acidic reaction), humus content of at least 2%, carbonate content not higher than 12–15%. |
| Minimum distance from other trees | For dwarf 2.5 m, for the other 4 m |
| Pollinator availability | Mandatory (within a radius of no more than 50 m). In this role, it is recommended to use Suislepskoe, White filling, Melbu. |
Important! It is undesirable to plant a young apple tree in the same place where the old one used to grow: the fact is that in the soil after such a tree there remains a high content of floridzin - glycoside harmful to the seedling. But after cherries or plums Lingonberry can be planted.
The apple tree grows well on loam, sandstone, chernozem, and floodplain soil. But on the salt marshes, swamped peat bogs, podzolic soil, alumina or red earth, the development of the tree will be inhibited.
Lingonberry seedling, like any other fruit tree, should be purchased exclusively in specialized garden nurseries, and a similar organization is best found in the same area where the planting will be carried out: in this case, the tree will experience less stress from the transplant and take root much better.

The optimal age for planting an apple tree is a one-year or two-year-old. It can be determined by growth: the maximum trunk length of such a seedling should not exceed 1–1.2 m, and if the tree is grafted onto a dwarf rootstock, then it can be slightly less than the specified parameter.
When buying a lingonberry sapling, you need to ask what stock it is grafted on. The best option for this variety is considered M9 - a traditional dwarf rootstock, significantly increasing the productivity of the apple tree, preserving the compactness of the tree and increasing its lifespan.
The best time for planting Lingonberry is spring, although the autumn version of planting fans is also a lot. In the first case, the tree should be planted before flowering begins, in the second - before the transition of the apple tree to a dormant state, immediately after dropping the leaves.
The landing pit is traditionally prepared in advance - at least 2-3 weeks before the expected landing. The volume of the pit depends on the size of the root system of the seedling, but approximately can be 90-100 cm in depth and about the same in width.

The lower layer of the earth extracted from the pit should be removed, and the upper layer should be fertilized by mixing with the following components:
- organic fertilizer (you can use compost or humus; fresh manure is not suitable for this purpose, only completely rotted) - 2-3 buckets;
- peat (sand) - 1/2 bucket;
- wood ash - 500-700 ml (potassium sulfate can be used, in this case, approximately 250 ml of the drug is sufficient);
- ammonium nitrate - 1/3 cup;
- vermicompost - 300-500 ml;
- superphosphate - 250 ml (can be replaced with phosphorite flour, reducing the amount of funds by 30%).
Check out more

After acquiring a seedling, its root system should be dipped in a clatter prepared from 1 part of rotted manure and 2 parts of clay mixed with water until the consistency of thick sour cream, and then let the roots dry out a little.
In the meantime, the soil at the bottom of the pit should be raked to the center and a wooden stake should be driven in the middle of the pit under the future support for the tree.
The stake height should be calculated so that it is not much lower than the seedling itself. The prepared tree should be installed next to the support with the vaccination site to the south, the roots should be straightened on the slopes of the hill built at the bottom of the pit.
When falling asleep, it is necessary to stop from time to time and compact the soil. After planting, the root neck should remain above the ground at a height of about 5-6 cm.
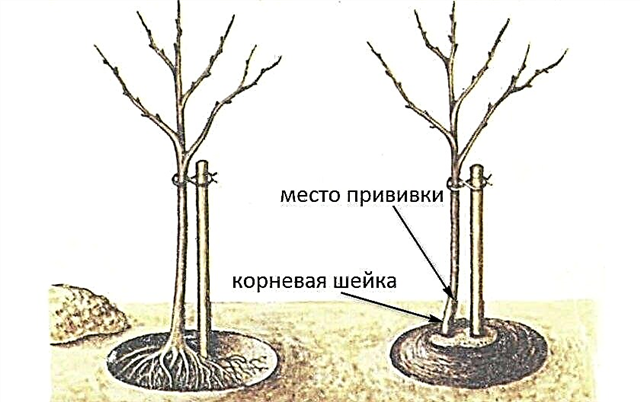 For the correct planting of an apple tree, 2 people need to participate: while one is digging a hole, the second should constantly hold the seedling, periodically pulling it up, as if to avoid the formation of air jams in the soil.
For the correct planting of an apple tree, 2 people need to participate: while one is digging a hole, the second should constantly hold the seedling, periodically pulling it up, as if to avoid the formation of air jams in the soil.
When this condition is met, the trunk should be watered abundantly and mulched immediately after absorbing water. At the end of the work, the seedling should be tied to a support using a soft twine or rope (wire should not be used so as not to damage the bark).
Plant care
A high and stable yield of the Lingonberry apple tree is guaranteed only when the tree is properly maintained. This variety can not be called unpretentious.
Recommended

- crop rationing;
- formative, sanitary, and subsequently - anti-aging pruning;
- watering;
- top dressing;
- soil care (removal of weeds, fallen fruits and leaves, loosening, mulching);
- preventive, and if necessary - treatment for diseases and pests.
Watering the apple tree
Lingonberry variety is not very drought tolerant.Moreover, with a lack of moisture in the soil, the yield of the bonsai can be significantly reduced. For this reason, it is recommended to water the area of the near-trunk circle during the July heat every 10 days, spending at least 4-5 buckets of water heated in the sun.

In addition, to keep the soil moisture longer, use one of the following techniques:
- Carefully and carefully (so as not to damage the surface roots of the tree) to loosen the soil and at the same time remove weeds.
- Mulch the near-stem circle with straw, peat, sawdust or other moisture-retaining organics. At the same time, the mulch layer needs to be periodically replenished, since over time it rotts in the lower part.
- To plant a piece of land under the apple tree with siderates (lupine, white mustard, etc.), meadow grass or vegetable or ornamental plants with a shallow root system, which will preserve the natural looseness of the soil and, in case of using siderates, will additionally saturate it with nitrogen and other useful elements.
Did you know? The smallest apple tree in the world grows in New Zealand and is called Tiddly Pomme. The weight of such an apple varies between 40-50 g, and the fruit itself easily fits in a teaspoon.
Fertilizer application
Proper feeding of Cowberry is a prerequisite for good productivity. However, it is not necessary to oversaturate the soil under the apple tree with fertilizers, since the harm from this can be much greater than from a lack of fertilizing.

Regardless of whether an apple tree was planted in spring or autumn, it is not necessary to fertilize it during the first year after planting. During this period, the tree needs to take root, and the introduction of additional nutrients into the soil will only interfere with this process.
Then, fertilizer application is carried out according to the classical scheme: the nitrogen component is used in the spring, during the period of active vegetation, and the potash and phosphorus components are used in the autumn, before the tree goes to rest and as an apple tree preparation for winter. Organics in the soil can be applied both in spring and in autumn.

If we talk about the most famous mineral fertilizers (including complex), then, based on one small tree, their dosage should be as follows:
- ammonium nitrate - 50–80 g;
- carbamide - 40–70 g;
- potassium chloride - 45–80 g;
- potassium sulfate - 80-100 g;
- wood ash (potassium source) - 1–1.5 kg;
- superphosphate - 120-150 g;
- phosphorite flour - 150-180 g;
- ammophos (nitrogen + phosphorus) - 200-300 g;
- nitroammophosk (nitrogen + phosphorus + potassium) - 200-300 g.

In addition to the well-known “Biohumus”, such funds include, for example, such trade names:
- "Phosphorobacterin";
- "Shine-1"
- Rizotorfin;
- "Rhizoenterin";
- "Rhizoagrin";
- Mizorin;
- “Productive economies”;
- "Economics Bioconstructor";
- "Flavobacterin";
- "Baikal EM1".
Important! Unlike tall apple trees, dwarf varieties need 1 additional top dressing in June. During this period, the tree should receive 150 g of potassium, 250 g of phosphorus and 150 g of nitrogen (the norms of the active substance, not the drug, are indicated).
The use of such funds not only provides a higher and more stable yield, but also increases the resistance of the tree to various fungal diseases, in particular, rhizoctonia and fusariosis.
Crown pruning
Despite the fact that Lingonberry is a dwarf tree, regular pruning of this apple tree is needed just like any other. This procedure is necessary to improve sap flow and increase plant resistance to various diseases, as well as to more convenient care for it. The sparse-tier method of pruning, which is usually used for tall-growing apple trees, is not very suitable for a weeping dwarf tree.

Therefore, a different principle is used here, consisting of the following:
- The first year after planting - shorten the conductor by about 15–20%.
- The second and several subsequent years (until the tree reaches its natural size) - cut the strongest annual growths to 20%, so that they all have approximately the same length. The remaining branches should be removed at the base of the trunk, “onto the ring” (hemp should not be left).
- Constantly control that the skeleton of the tree does not have exposed sections, and the main side branches are evenly distributed over the entire diameter and height.
- The shoots appearing below the vaccination site should be removed immediately.
- The adult tree is no longer forming. He only needs to do sanitary pruning, that is, remove dry, damaged, curved, diseased and clearly interfering branches.
Important! The main goal of the forming pruning of the apple tree is to ensure uniform tree development from all sides.
Formative pruning should be done at the end of winter or at the beginning of spring, on the eve of activation of sap flow, and always before the buds begin to swell. Sanitary removal of unnecessary branches, on the contrary, is carried out in the summer or at the beginning of autumn, when the volume of work is very clearly visible. Branches affected by the fungus must be removed immediately, regardless of the season, so that the disease does not spread to the entire apple tree.
Winter preparations
 Lingonberry variety is distinguished by high winter hardiness: the plant withstands temperature drops to –40 ° C, and also rarely suffers from spring back frosts or early autumn cold snap. Therefore, there is no need to shelter an adult apple tree for the winter, but such a precaution will not hinder the seedling.
Lingonberry variety is distinguished by high winter hardiness: the plant withstands temperature drops to –40 ° C, and also rarely suffers from spring back frosts or early autumn cold snap. Therefore, there is no need to shelter an adult apple tree for the winter, but such a precaution will not hinder the seedling.
The stamp from the root of the neck itself can be wrapped with any light material that allows air to pass through. For shelter, burlap, agricultural fiber, old women's tights or stockings are suitable.
In addition, the trunk circle itself is worth sheltering. To do this, it is better to use the same material that is mulching (peat, sawdust, straw), but the layer needs to be made much thicker.
After snowfall, it will also be useful to build an additional blanket around the tree in the form of a snowdrift: in addition to heating, it will provide additional moisture to the soil in spring, when the snow begins to melt.
Important! Dark material for sheltering a seedling is not suitable for winter, because during the thaw or sunny winter days, the tender bark under the light-attracting shelter will scatter and, accordingly, lose its structure.
If soldering foliage is used for shelter, before laying it, the ground must be covered with agrotechnical fiber or other air-permeable material, and after the sun warms up, immediately remove from the site. These precautions are associated with the fact that numerous pests and spores of fungi winter in the fallen leaves, which are activated in the spring.

To survive the winter a young seedling will help the correct rationing of the fruits. As it was said, Lingonberry begins to bear fruit already starting the next year after planting, however, it is not worthwhile to allow this to the gardener: the process of setting and ripening the fruits takes a lot of energy from the tree (15 times more than the growth of leaves and shoots), therefore, by the fall, vitality such an apple tree will be very weak.
Experts recommend removing about half of the ovaries in the next 3-5 years after planting, especially if Lingonberry is grown in regions with cold and little snowy winters. Preparation for the winter of an adult apple tree includes 2 important procedures: the full cleaning of fallen leaves and fruits throughout the area around the tree, as well as plentiful watering with not too cold water on the eve of the first frosts.
Diseases and Pests
With moderate scab resistance, Cowberry is less protected from some other fungal infections. Particularly high probability of infection of the tree in conditions of high humidity (for example, if the summer turned out to be cool and rainy). Also, dwarf apple trees are often the target of pest attacks.

In particular, the gardener needs to be prepared in time to recognize signs of problems that may arise with the tree:
| Dwarf apple tree diseases | Insects and other pests that parasitize on the apple tree |
| Cytosporosis | Apple Blossom |
| Rhizoctonia | Aphids (green apple, green rose, red gall gray, peach, cherry, etc.) |
| Fusarium | Apple tinker |
| Scab | Apple Moth |
| Powdery mildew | Moth (apple, plum, oriental, pear) |
| Sooty mushroom | Red fruit tick |
| Rust | Leaflet |
| Rot (stem, fruit, gray) | Scoops |
| Spotting (white, brown) | Hawthorn |
| Black cancer | Fruit sawfly |
Preventative treatment of the tree is best carried out in the spring, and 1 spraying, even with a very effective drug, is not enough. The fact is that the activation of various pests and diseases does not take place simultaneously, and therefore, destroying some pathogens, the pesticide is completely useless in relation to others.
Did you know? Caterpillars are incredibly voracious: over the entire period of existence in the larval phase, an insect can increase its body weight by 50 thousand times. Since not a single skin cover can withstand such a load, the caterpillar molts several times, changing its “skin" to a larger size.
Traditionally, 3 spring treatments are carried out:
- “On a green cone” (before swelling of the kidneys) - during this period, the spores of many fungi and the larvae of insects that overwintered in the cortex are destroyed;
- after the leaves bloom, but before flowering begins;
- immediately after flowering.
It is not recommended to treat apple trees in summer with potent drugs, as this can affect the quality of the crop. If diseases or pests have manifested themselves during this period, you can use biological agents such as Fitoverm, Haupsin, Fitodoctor, Trichodermin, Fitosporin M, etc.

For conventional treatments, a fungicidal or insecticidal preparation should be selected individually, based on which diseases and pests are rampant in this region (any gardener, based on past experience, knows the answers to these questions well).
In particular, spring spraying of the apple tree can be carried out using:
- carbamide;
- iron or copper sulfate;
- Bordeaux mixture (copper sulfate is also its basis, but lime is also present in the preparation to improve contact with the tree);
- colloidal sulfur.
Modern industry offers a huge number of preparations for processing orchards, for example:
Recommended Reading

- "Fufanon";
- Tiovit Jet;
- "Spark";
- "Clean Garden";
- "Topaz";
- "Speed";
- Home
- "Fundazole";
- "Sentinel";
- "Gates";
- "Spark";
- "Calypso";
- Kinmix
- Inta-Vir;
- "Karate" and many others.
Harvesting and storage
Speaking about the disadvantages of the Lingonberry variety, they sometimes call the short shelf life of the crop. However, this estimate is incorrect. In fact, the fruits of Lingonberry are stored approximately as much as is necessary for varieties of early autumn ripening.
Important! For long-term storage, only the so-called late-winter apples, ripening in mid-October, are used. Winter varieties are stored for up to six months (ripening period is early October). Further, the earlier the fruit ripens, the shorter their shelf life.
Given the very high yield of the variety, apples are recommended to be removed in several stages, each time picking the most ripe fruits. This will allow you to somewhat stretch the period of their use. However, it should be remembered that, despite the low weight, cranberries are very prone to premature shedding due to the thin and weak stalk, and the carrion is not suitable for storage at all. Therefore, pulling with the harvest is also not worth it.

If necessary, use the Lingonberry crop for processing (drying, freezing, canning or urinating), you need to do this as soon as possible after removing the fruits from the tree - preferably on the same day or at least the next. The fact is that during storage, the nutritional and taste characteristics of fruits are very rapidly reduced.
Variety of apple trees Lingonberry is an excellent choice for owners of small land plots. A small tree, which at the same time gives a truly huge harvest of beautiful and tasty red-sided fruits, will not only serve as a source of vitamins, but can also become a real decoration of the garden, especially during fruiting.